| Jonathan Andreas |
Bluffton University |
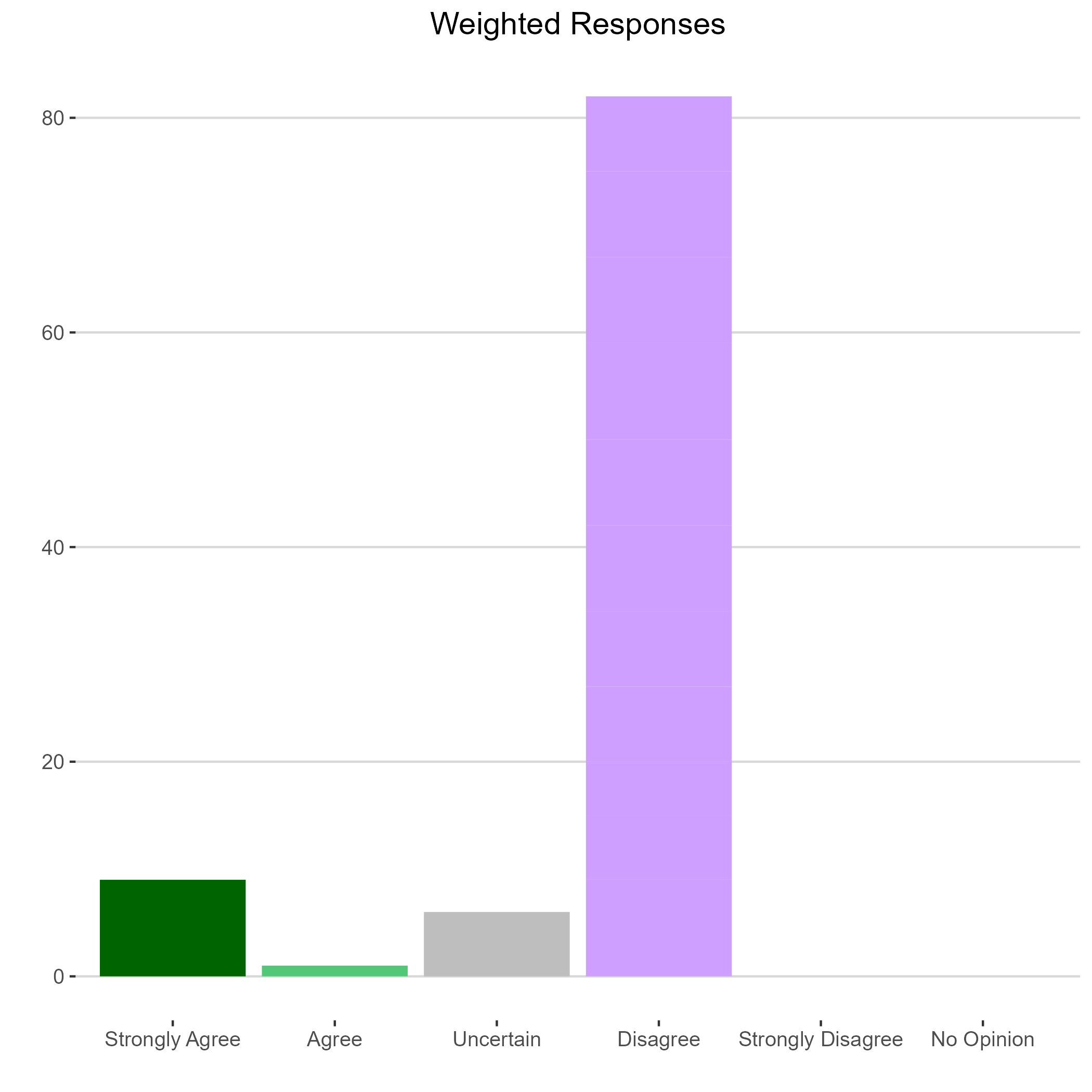
Agree |
1 |
This question may have left out some implied context making it difficult to answer. A tax cut almost always reduces tax revenues, and by itself, this will definitely reduce revenues. But I think you might have been wanting to ask about the overall tax package which modestly increased taxes on higher-income earners making the overall effect of the tax changes fairly revenue neutral. |
| Ron Cheung |
Oberlin College |
Disagree |
7 |
|
| Kevin Egan |
University of Toledo |
Disagree |
7 |
I expect state tax revenues to be slightly lower, which could be offset by other more efficient taxes, such as corrective taxes on gasoline or alcohol that could then fund efficient state programs such as subsidizing high quality pre-k education programs for children. |
| Paul Holmes |
Ashland University |
Strongly Agree |
9 |
Imagining we're on the right hand side of the Laffer curve is... a real laugher. |
| Michael Jones |
University of Cincinnati |
Disagree |
8 |
|
| Charles Kroncke |
Mount Saint Joseph University |
Disagree |
5 |
|
| Trevon Logan |
Ohio State University |
Disagree |
9 |
Given high MPC and consumption taxes, it is not clear that state tax revenue suffers. |
| Diane Monaco |
Economics Professor |
Disagree |
7 |
In 2017, the Ohio General Assembly eliminated state income tax rates for taxpayers earning less than $10,650, and then legislators continued to lower tax rates for taxpayers earning less than $26,000 where there were still no state income taxes! 41 states have an individual income tax rate on wages and income. State income tax rates range from 1.4% -11% and are in general 40% of overall state tax collections. What is even more important is that state income tax brackets are generally comparable among states, although income tax brackets for higher income earners play a much greater role. Overall state income tax rates tend to be relatively more progressive than the Federal (IRS) income tax rates that are more likely to offer compromises on settling tax debt for less debt than the full amount. However, state level income tax collectors quite often and unexpectedly push struggling income taxpayers even deeper into debt hardship. |
| Joe Nowakowski |
Muskingum University |
Disagree |
6 |
|
| Curtis Reynolds |
Kent State University |
Disagree |
8 |
The key word is "significantly." Tax revenues may be lower because of this, but they are also lower because of tax cuts to other parts of the income distribution. |
| Kay Strong |
Independent |
Disagree |
9 |
Low income taxpayers contribute minimally to the tax base |
| Ejindu Ume |
Miami University |
Uncertain |
6 |
|
| Kathryn Wilson |
Kent State University |
Disagree |
8 |
There will be significantly lower state tax revenues because of the changes, but this is driven by the reduction in tax rates across all income levels and the elimination of the top tax rate. The reduction in income from the expansion of the 0% income tax bracket for lowest earners will be small in absolute terms and relative to the overall reduction in tax revenue. |